Welding is crucial in many industries, including construction, manufacturing, and repair work. It involves intense heat, bright light, flying sparks, and exposure to harmful fumes and gases. Without proper protection, welders face serious risks of injuries and long-term health issues. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, thousands of welding-related injuries occur annually, many of which could have been prevented by using proper PPE. Investing in high-quality PPE and enforcing its use is a legal requirement and a critical step in creating a safe working environment for welders.'
This comprehensive guide will cover the must-have welding PPE from head to toe. We'll explore the different types of protective gear, their features, and how to select the right equipment for specific welding applications.
Top Welding Personal Protective Equipment to Own
Welding Helmets
Welding helmets are arguably the most crucial piece of PPE for welders. This protective headgear shields the face, eyes, and neck from the intense light, heat, and flying sparks generated during welding.
Types of Welding Helmets and Their Features
Various types of welding helmets are available, each designed for specific welding applications and conditions. Some common options include:
Fixed-shade helmets: These helmets have a fixed-tint lens that always remains dark, suitable for certain low-amperage welding tasks.
Auto-darkening helmets: These feature an auto-darkening filter lens that adjusts its shade level based on the welding arc's intensity, providing better visibility and protection.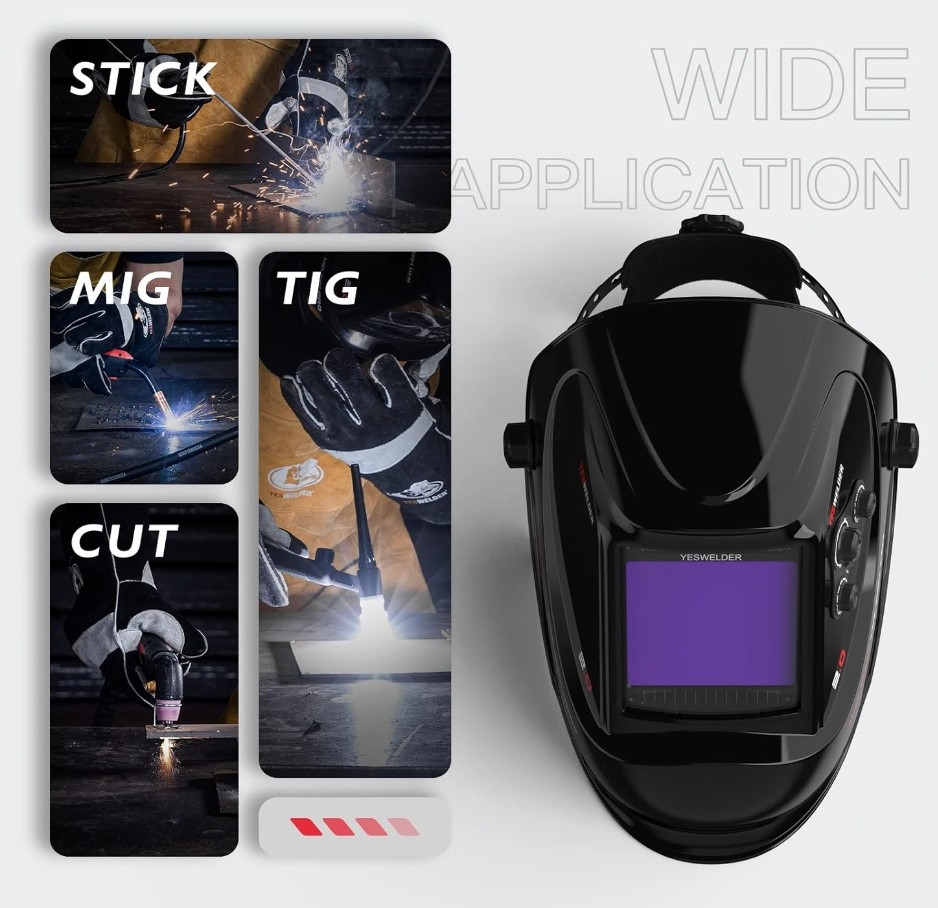
Passive helmets: These welding helmets have a fixed-shade lens that requires manual switching between light and dark states, typically used for oxyfuel welding and cutting.
Welding helmets often incorporate additional features for improved safety and comfort, such as:
- Adjustable headgear for a secure and comfortable fit
- Replaceable lens covers to protect the main lens from scratches and spatter
- Exhaust vents for improved air circulation and reduced fogging
Considerations for Selecting the Right Welding Helmet
When choosing a welding helmet, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal protection and performance:
Welding process and amperage range: Different welding processes and amperages require specific lens shade numbers for proper eye protection.
Work environment: Factors like confined spaces, outdoor conditions, or overhead welding may influence the helmet's design and features.
Personal preference: Helmet weight, viewing area, and adjustability can impact comfort and productivity during extended welding sessions.
Selecting a welding helmet that meets or exceeds applicable safety standards, such as those set by ANSI (American National Standards Institute) or other relevant organizations, is essential. Regular inspection and maintenance of the helmet are also crucial to ensure its continued effectiveness in protecting the welder's head and face.
Welding Safety Glasses & Face Shields
Welding safety glasses and face shields are essential for welders' eye and face protection. These specialized pieces of PPE are designed to safeguard against various hazards that can cause severe eye injuries, including intense ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation, flying sparks, and molten metal splashes.
Welding safety glasses come in different styles and configurations, each serving a specific purpose:
- Cover goggles: These lightweight glasses feature contoured lenses that provide complete eye coverage and protection from debris and splatter. They are often used in combination with a face shield for added protection.
- Spectacles: Welding spectacles resemble regular glasses but feature impact-resistant lenses with appropriate shade numbers for welding applications. They offer good peripheral vision and are suitable for tasks that require more mobility.
- Welding goggle-spectacles: These hybrid glasses combine the features of goggles and spectacles, providing complete eye coverage while offering a panoramic view and improved ventilation.
Face shields protect the entire face from flying particles, sparks, and spatter. They are typically worn with safety glasses or goggles to ensure comprehensive eye and face protection.
Criteria for Choosing Suitable Welding Safety Glasses
When selecting welding safety glasses, several factors must be considered to ensure proper protection and comfort:
- Lens shade: The lens shade number should be appropriate for the specific welding process and amperage range. Darker shades are required for higher amperage welding to protect against intense light radiation.
- Lens material: Common lens materials include polycarbonate, CR-39 plastic, and glass. Polycarbonate lenses are lightweight, impact-resistant, and offer good optical clarity, making them popular.
- Lens coatings: Various coatings can be applied to welding safety glasses to enhance performance. Anti-fog coatings prevent lens fogging, while scratch-resistant coatings improve durability.
- Fit and comfort: Proper fit is crucial to ensure the glasses remain secure during welding activities and to prevent gaps that could allow debris or radiation to enter. Adjustable features like nose pads and temple arms can improve comfort during prolonged wear.
Choosing welding safety glasses and face shields that comply with relevant safety standards, such as ANSI Z87.1 or EN 166, is essential. They ensure to provide sufficient protection against the particular hazards faced in welding environments.
Respiratory Protection
Welding often generates hazardous fumes, gases, and particulate matter that can harm a welder's respiratory health if inhaled. These airborne contaminants can cause various short-term and long-term respiratory issues, ranging from irritation and coughing to more severe conditions like metal fume fever, lung cancer, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Proper respiratory protection is crucial in welding environments to prevent inhaling these harmful substances. Failure to use appropriate respiratory protective equipment (RPE) can lead to acute and chronic respiratory problems. These can potentially result in permanent lung damage and other life-threatening conditions.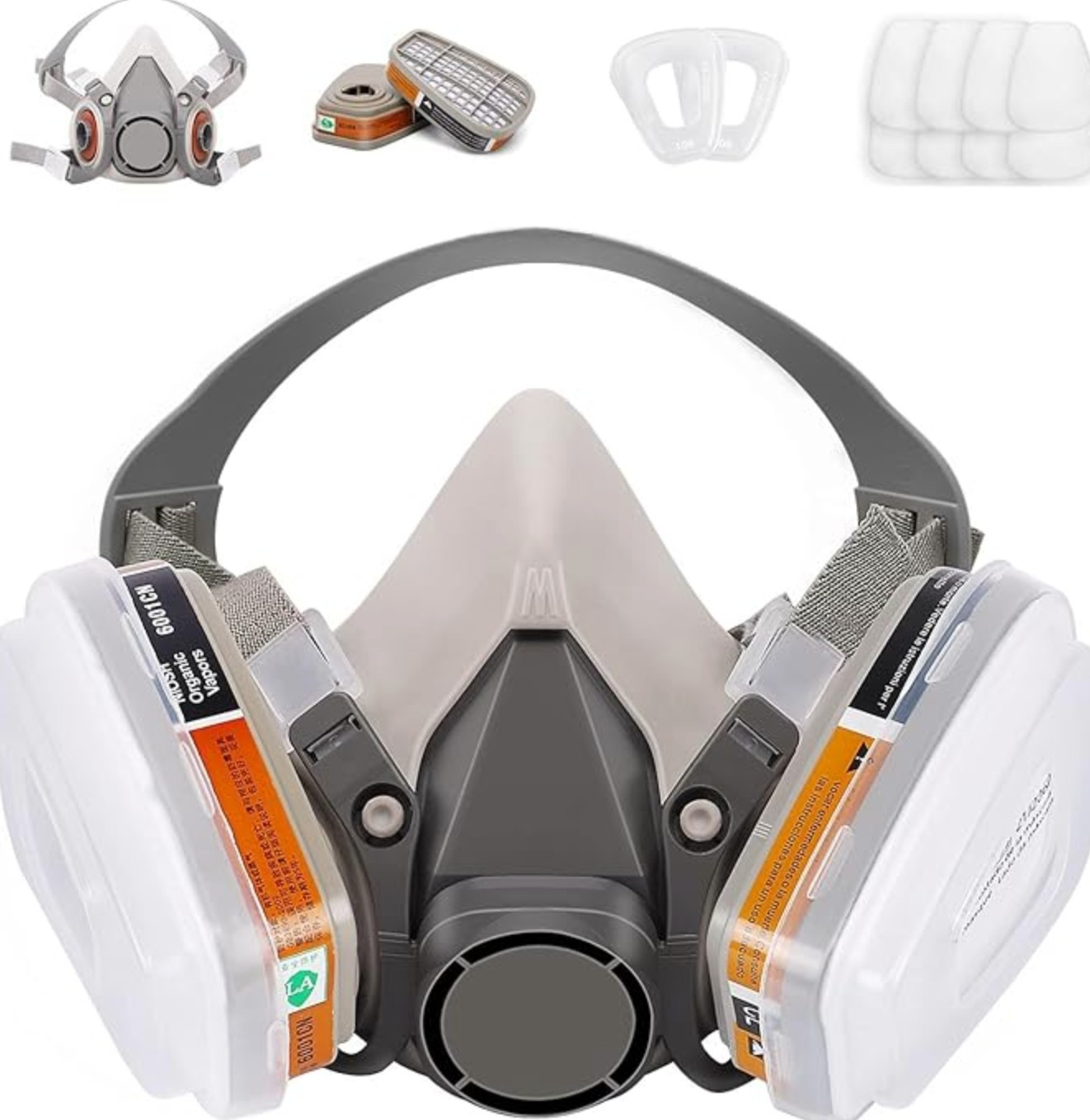
Different Types of Respirators and Their Effectiveness
Welders have access to various types of respirators, each offering different levels of protection depending on the specific welding process, the contaminants present, and the concentration of those contaminants. Some common types of respirators used in welding include:
Disposable particulate respirators: These lightweight respirators are designed to filter out particulate matter, such as metal fumes and dust. They offer basic protection and are suitable for lower-risk welding applications.
Half-mask respirators: These reusable respirators cover the nose and mouth and are equipped with replaceable cartridges or filters that capture particulates, gases, and vapours. They provide a higher level of protection than disposable respirators and are suitable for many welding tasks.
Full-face respirators: These respirators cover the entire face, including the eyes, and offer the highest level of protection against airborne contaminants. They are recommended for welding processes that generate high levels of hazardous fumes or gases or when working in confined spaces with poor ventilation.
Powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs): PAPRs use a battery-powered blower delivers filtered air to the welder's breathing zone, providing a constant clean air flow. They are suitable for prolonged welding tasks or work in extremely hazardous environments.
Welding Gloves
Welding operations expose a welder's hands to hazards, including intense heat, molten metal splashes, sparks, and sharp edges. Without proper hand protection, welders risk sustaining severe burns, cuts, and other injuries that can lead to permanent damage or disability.
Also Read - Welding Safety Rules
Welding gloves are essential personal protective equipment (PPE) that safeguard a welder's hands from these hazards. They provide a barrier against heat and sharp objects and offer grip and dexterity, allowing welders to perform their tasks safely and efficiently.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Welding Gloves
When selecting welding gloves, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal protection and performance:
Welding process: Different welding processes generate varying heat levels and exposure to molten metal. Gloves designed for high-heat applications, such as stick welding or oxyfuel welding, require greater heat resistance than those used for lower-heat processes like MIG or TIG welding.
Material: Welding gloves are made from leather, Kevlar, or specialized fabrics like Nomex or Preox. Leather gloves offer good heat resistance and durability, while Kevlar and other synthetic materials provide superior cut and abrasion resistance.
Insulation: The level of insulation in welding gloves determines their ability to protect against extreme heat. Gloves with additional insulation layers, such as wool or aluminium lining, are recommended for high-heat welding tasks.
Cuff length: Longer cuff lengths provide additional protection for the wrists and forearms, which are also vulnerable to burns and sparks during welding.
Dexterity and grip: Welding gloves should allow for sufficient dexterity and grip to handle tools and materials safely and efficiently. Gloves with reinforced palms and fingertips can improve grip and extend the glove's lifespan.
Compliance with standards: Choosing welding gloves that meet or exceed relevant safety standards, such as ANSI/ISEA 105 or EN 12477, is essential to ensure they provide adequate protection against the specific hazards encountered in welding environments.
Welding Jackets
Welding operations expose workers to numerous hazards that extend beyond just the hands and face. The intense heat, molten metal splashes, and flying sparks generated during welding can also cause severe burns and injuries to other parts of the body, particularly the torso, arms, and legs.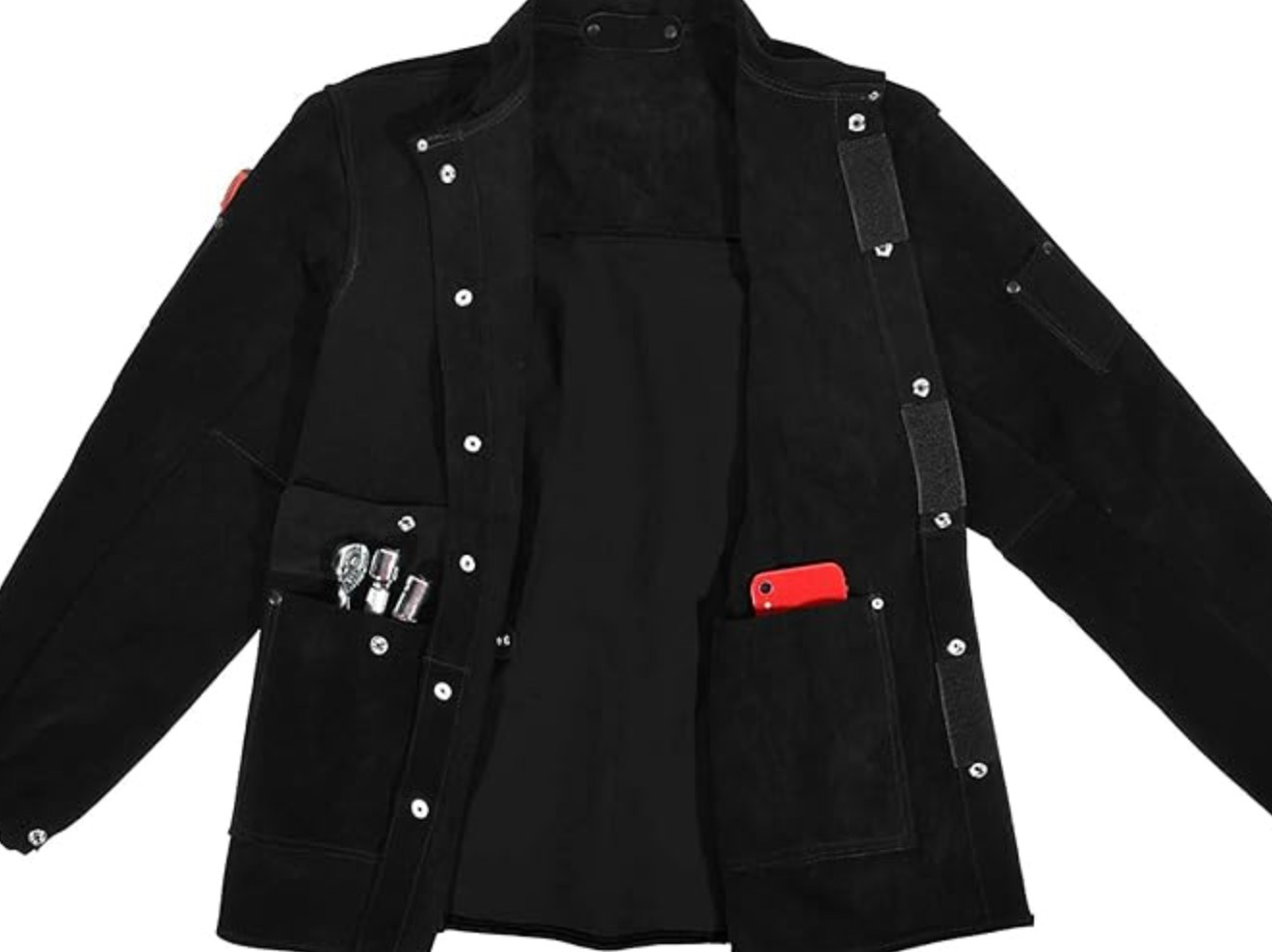
Body protection is crucial in ensuring the overall safety of welders, and welding jackets play a vital role in this regard. These specialized garments are designed to provide a protective barrier against the various hazards encountered in welding environments, shielding the welder's body from potential harm.
Characteristics of Effective Welding Jackets
Effective welding jackets possess several key characteristics that contribute to their protective capabilities and overall performance:
- Heat and flame resistance: Welding jackets are made from leather, flame-resistant cotton, or specialized fabrics like Nomex or Kevlar. These materials offer excellent heat and flame resistance, ensuring the jacket can withstand exposure to high temperatures and molten metal splashes without igniting or compromising its protective properties.
- Insulation: Many welding jackets incorporate insulating layers or linings, such as wool or aluminium, to protect against intense heat and prevent burns from prolonged exposure.
- Durability: Welding environments can be harsh and demanding, subjecting protective clothing to wear and tear. Durable welding jackets are designed to withstand these conditions, featuring reinforced areas and sturdy construction to ensure longevity and reliable protection.
- Proper coverage: Effective welding jackets should provide ample coverage for the welder's body, including the arms, shoulders, and upper legs. Longer jackets or jackets with adjustable cuffs or leg guards offer additional protection for vulnerable areas.
- Ventilation: While protection is paramount, welding jackets should also allow adequate ventilation to prevent overheating and discomfort during prolonged welding sessions. Features like vents, mesh panels, or moisture-wicking fabrics can help regulate body temperature and promote airflow.
- Ease of movement: Welding often requires various body movements and positions, so welding jackets should allow for a full range of motion without restricting the welder's ability to perform their tasks safely and effectively.
By selecting a welding jacket that meets these characteristics and complies with relevant safety standards, welders can ensure comprehensive body protection, minimizing the risk of burns, injuries, and other hazards associated with welding operations.
Welding Boots
While welding primarily involves working with hands and tools, the feet and legs are also vulnerable to various hazards in welding environments. Molten metal splashes, heavy objects, and sharp materials can easily cause burns, cuts, and other foot injuries if proper protection is not in place.
Welding boots are an essential component of personal protective equipment (PPE) for welders, as they provide critical protection for the feet and lower legs. Without appropriate foot protection, welders risk sustaining severe injuries that can compromise their safety and ability to perform their jobs effectively.
Features to Look for in Welding Boots
When selecting welding boots, several key features should be considered to ensure adequate protection and comfort:
- Heat and flame resistance: Welding boots should be made from heat-resistant and flame-retardant materials, such as leather or specialized fabrics like Kevlar or Nomex. These materials can withstand exposure to high temperatures and molten metal splashes without compromising their protective properties.
- Metatarsal guards: Many welding boots incorporate metatarsal guards, reinforced areas that protect the top of the foot from falling objects or heavy impact. This feature is particularly important in environments with a risk of dropped tools or materials.
- Steel or composite toe caps: Steel or composite toe caps provide additional protection against impact and compression, safeguarding the toes from injuries caused by falling objects or heavy loads.
- Slip resistance: Welding environments can be slippery due to oils, spills, or debris. Welding boots should have slip-resistant outsoles to provide adequate traction and prevent slips and falls, which can lead to serious injuries.
- Puncture resistance: Some welding boots feature puncture-resistant insoles or midsoles, which protect the feet from punctures by sharp objects or debris on the ground.
- Ankle support: Welding often involves standing or working in awkward positions for extended periods. Boots with good ankle support can help prevent sprains and provide stability, reducing the risk of injuries.
- Electrical hazard protection: In certain welding applications, such as working near live electrical circuits, welding boots with electrical hazard protection can prevent potential electrical shocks or burns.
- Comfort and breathability: While protection is paramount, welding boots should prioritize comfort and breathability. Features like moisture-wicking linings, cushioned insoles, and proper ventilation can help minimize fatigue and discomfort during prolonged wear.
By selecting welding boots that meet these criteria and comply with relevant safety standards, welders can ensure their feet are adequately protected against the various hazards encountered in welding environments, allowing them to work safely and efficiently.
Ear Plugs and Ear Muffs
Welding processes often generate high noise levels, posing a significant risk to a welder's hearing health. The intense sounds produced by welding equipment, such as grinders, plasma cutters, and arc welding machines, can reach dangerously high decibel levels, particularly in enclosed or poorly ventilated spaces.
Prolonged exposure to excessive noise levels can lead to various hearing-related issues, including temporary or permanent hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and psychological effects like stress and fatigue. These conditions impact a welder's quality of life and can compromise their ability to communicate effectively and follow safety protocols in the workplace.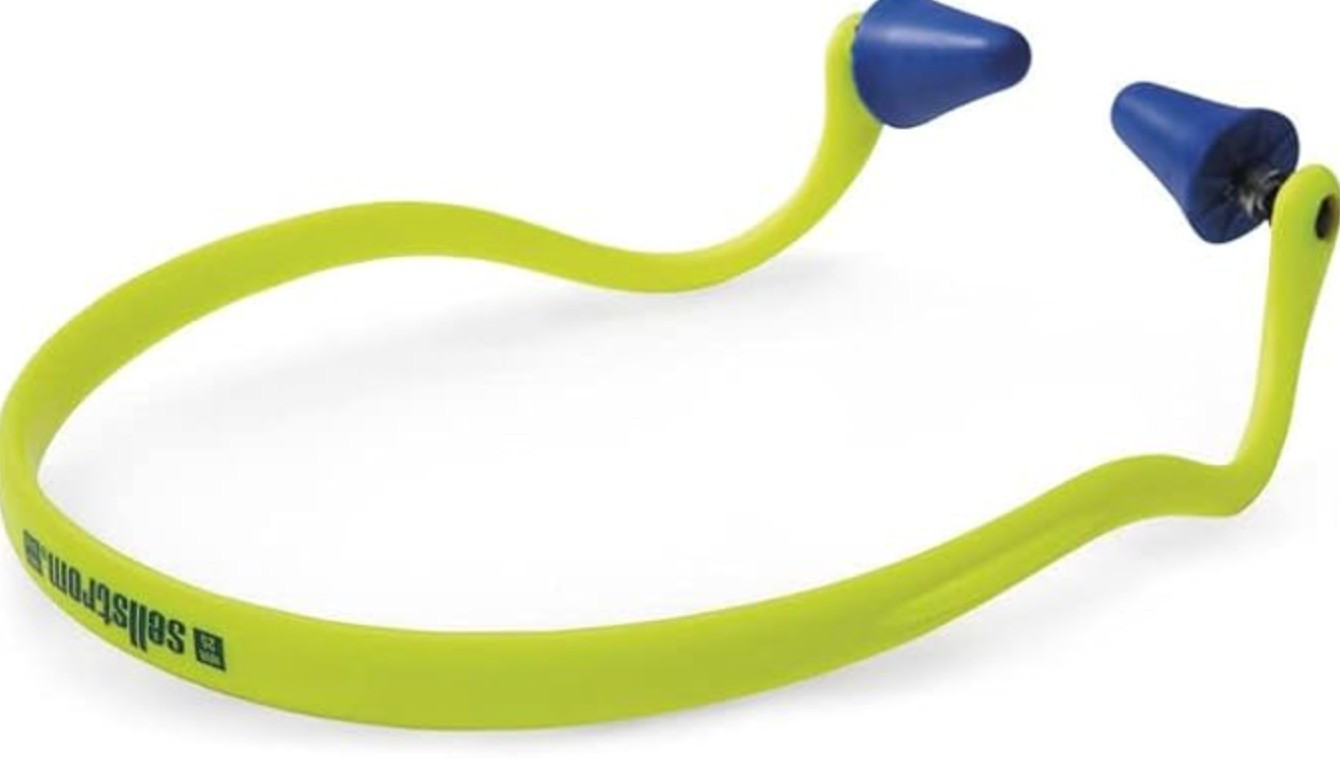
Choosing the Right Hearing Protection Devices
To reduce noise exposure in welding environments, it is crucial to use appropriate hearing protection devices (HPDs). Two common types of HPDs used in welding are ear plugs and ear muffs, each offering distinct advantages and suitable for different situations.
Ear Plugs:
- Ear plugs are small, compact devices inserted directly into the ear canal to block out noise.
- They are available in various materials, including foam, silicone, and moldable wax or putty.
The advantages of earplugs include their portability, ease of use, and compatibility with other PPE, such as welding helmets or respirators.
- Ear plugs are particularly suitable for welding tasks that require mobility or working in confined spaces.
Ear Muffs:
- Ear muffs are larger, over-the-ear devices that cover the entire ear and create a noise-blocking seal around the ear cup.
- They typically feature adjustable headbands and cushioned ear cups for improved comfort during extended wear.
- Ear muffs offer a higher noise reduction level than ear plugs and are often preferred for extremely loud environments or prolonged exposure.
- They are also beneficial for welders who may need to frequently remove and reapply their hearing protection during their work shifts.
Additional Protective Equipment
Welding Screens and Curtains
In addition to personal protective equipment (PPE) worn by welders, welding screens and curtains serve as important barriers to protect others in the vicinity from the hazards associated with welding operations. These auxiliary protective devices are crucial in creating a safe working environment for welders and nearby personnel.
1. Welding Screens:
Welding screens are portable barriers that shield individuals from the intense light, sparks, and UV radiation generated during welding. They are typically constructed from flame-resistant and lightweight materials, such as fibreglass or welding blankets, and can be easily positioned around the welding area.
The primary functions of welding screens include:
- Blocking harmful UV and infrared radiation, preventing eye damage and skin burns.
- Containing sparks and molten metal splatter, reducing the risk of fires or injuries.
- Providing a visual barrier to prevent bystanders from being exposed to the bright welding arc.
Welding screens are particularly useful when welding operations are conducted near other workers or in high-traffic zones, ensuring that non-welding personnel are adequately protected.
2. Welding Curtains:
Welding curtains are similar to screens but are designed to be hung from ceilings or mounted on walls, creating a more permanent barrier around the welding area. These curtains are typically made from heavy-duty, flame-resistant materials such as vinyl or treated canvas.
In addition to providing the same protective functions as welding screens, curtains offer additional benefits:
- Defining dedicated welding areas and separating them from other work zones.
- Containing fumes and smoke within the welding area, improving air quality in the surrounding workspace.
- Providing a physical barrier that can help prevent accidental entry into the welding area.
Welding curtains are particularly useful in enclosed spaces or areas with limited ventilation, as they help contain welding fumes and prevent their spread to other parts of the facility.
Both welding screens and curtains should be regularly inspected and maintained to ensure they are in good condition and free from damage that could compromise their effectiveness. Following proper setup and positioning guidelines is essential to maximize their protective capabilities.
Protective Clothing
While welding PPE such as helmets, gloves, and jackets provide targeted protection for specific body parts, protective clothing offers an additional layer of overall body coverage and protection against welding hazards.
1. Flame-Resistant Clothing:
Welding generates intense heat, sparks, and the risk of potential fire hazards. Wearing flame-resistant clothing, such as overalls, coveralls, or specialized welding apparel, is crucial for protecting the welder's body from burns and preventing the ignition of regular clothing.
Flame-resistant clothing is typically made from materials like treated cotton, Nomex, or Kevlar, designed to self-extinguish and resist ignition when exposed to heat or flames. These garments provide a barrier against molten metal splashes, sparks, and other potential ignition sources.
2. Leather Apparel:
In addition to flame-resistant fabrics, leather apparel, such as leather aprons, leggings, or sleeves, can provide excellent protection against heat, sparks, and molten metal splashes. Leather is a durable and heat-resistant material that can withstand high temperatures and prevent burns from short-term exposure to welding hazards.
Leather apparel is often worn with other PPE, providing additional coverage for areas not fully protected by welding jackets or gloves.
3. High-Visibility Clothing:
In some welding environments, such as construction sites or outdoor work areas, welders may need to wear high-visibility clothing. These garments are designed with reflective stripes or bright colours to ensure welders are easily visible to other workers or equipment operators, reducing the risk of accidents or collisions.
When selecting protective clothing for welding, it is essential to consider the specific hazards present in the work environment and the compatibility with other PPE worn by the welder. Proper fit, comfort, and breathability are important factors to ensure the welder can perform their tasks efficiently without compromising safety.
Regular inspections and replacement of protective clothing are necessary to maintain their effectiveness and ensure they provide adequate protection against welding hazards.
Why is Inspection and Maintenance of PPE critical for Welders?
Proper inspection and maintenance of welding personal protective equipment (PPE) ensures its effectiveness and longevity. Neglecting these practices can compromise the safety of welders and put them at risk of serious injuries.
Regular inspections of PPE are essential for identifying any potential defects, wear, or damage that may have occurred during use or storage. Here are some key reasons why regular inspections are important:
- Early detection of issues: Inspections allow for the early detection of problems such as cracks, holes, or degradation of materials, which can lead to reduced protection and potential hazards.
- Compliance with regulations: Many safety regulations and standards require regular inspections of PPE to ensure compliance and maintain a safe working environment.
- Preventing equipment failure: Regular inspections can prevent equipment failure during critical welding operations, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries by identifying and addressing issues early on.
Common inspection points for welding PPE include:
Welding Helmets - Lens condition, headgear adjustments, damage to shell
Safety Glasses - Lens scratches, frame integrity, proper fit
Respirators - Filter/cartridge condition, face seal integrity, exhalation valve function
Welding Gloves - Holes, tears, worn-out insulation, dexterity
Welding Jackets - Fraying, burn holes, reflective material condition
Welding Boots - Sole wear, toe cap integrity, metatarsal guard condition
Proper storage and handling of welding PPE
Proper storage and handling of PPE are essential for maintaining its condition and ensuring it remains effective. Factors to consider include:
- Storage environment: PPE should be stored in a clean, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Handling procedures: Proper handling techniques, such as avoiding dropping or dragging PPE on the ground, can prevent unnecessary damage.
- Segregation: Certain PPE items, like respirator cartridges or welding lenses, should be stored separately to avoid cross-contamination or damage.
Replacement guidelines and schedules:
Even with proper care and maintenance, PPE has a finite lifespan and must be replaced periodically to ensure continued protection. Replacement guidelines and schedules should be established based on factors such as:
- Manufacturer's recommendations: PPE manufacturers typically provide guidelines on when and under what conditions their products should be replaced.
- Usage frequency: PPE used more frequently or in harsher environments may require more frequent replacement.
- Inspection findings: If inspections reveal significant wear, damage, or degradation, immediate replacement may be necessary.
Maintaining accurate records of PPE inspections, usage, and replacements can help establish a reliable replacement schedule and ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Why Training and Compliance is Essential for Welders?
Providing adequate training and ensuring compliance with regulations and standards are essential components of a comprehensive welding safety program. These elements are crucial in promoting a strong safety culture and protecting welders from potential hazards.
Importance of PPE training:
Proper training on the selection, use, and maintenance of welding PPE is vital for several reasons:
- Understanding hazards: Training educates welders about the hazards associated with welding operations and the importance of using appropriate PPE.
- Correct usage: Welders learn to properly don, adjust, and wear PPE to ensure optimal protection and functionality.
- Maintenance and inspection: Training covers the necessary maintenance and inspection procedures to keep PPE in good working condition.
- Compliance: Comprehensive training helps ensure compliance with relevant safety regulations and industry standards.
Effective PPE training can take various forms, including:
- Classroom sessions: Theoretical knowledge and practical demonstrations.
- Hands-on training: Allowing welders to practice using and inspecting PPE under supervision.
- Refresher courses: Periodic refresher training to reinforce knowledge and address any updates or changes.
Compliance with regulations and standards:
Welding operations are subject to various safety regulations and standards established by organizations such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), and other industry-specific bodies.
Compliance with these regulations and standards is a legal requirement and essential for maintaining a safe working environment. Failure to comply can result in fines, legal liabilities, and increased risk of accidents and injuries.
Some key regulatory and standard requirements related to welding PPE include:
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910.252: Welding, Cutting, and Brazing - General Requirements
- ANSI Z49.1: Safety in Welding, Cutting, and Allied Processes
- ANSI Z87.1: Occupational and Educational Personal Eye and Face Protection Devices
- NFPA 51B: Standard for Fire Prevention During Welding, Cutting, and Other Hot Work
Promoting a safety culture:
Training and compliance efforts should be part of a broader initiative to foster a strong safety culture within the organization. A positive safety culture involves:
- Management commitment: Leadership must prioritize safety and allocate resources for training, PPE procurement, and compliance efforts.
- Employee engagement: Welders should be encouraged to actively participate in safety programs, report concerns, and suggest improvements.
- Continuous improvement: Regular reviews and updates to safety protocols, training programs, and PPE selection based on evolving best practices and industry developments.
Takeaway
Ensuring the proper use of welding personal protective equipment is paramount for the safety and well-being of welders. From head to toe, each piece of PPE plays a vital role in shielding workers from the various hazards associated with welding operations, including intense heat, bright light, flying sparks, harmful fumes, and loud noises.
By investing in high-quality PPE, implementing robust inspection and maintenance protocols, and providing comprehensive training, employers can create a safe and compliant working environment for their welding personnel. Additionally, fostering a strong safety culture that prioritizes PPE usage and encourages active participation from workers is crucial for successfully implementing a comprehensive welding safety program.
